Which Way Does A Zener Diode Go
Urinary blood thats visible only under a microscope microscopic hematuria is found when your doctor tests your urine. This Zener diode function makes it an excellent over-voltage security component.

The Zener Diode Working Principles And Its Various Applications
The Zener diode has a reverse-breakdown voltage at which the diode starts conductivity electric current and remains continuous in the reverse-bias mode.
Which way does a zener diode go. Forward Biased PN Junction Diode. When the voltage across the terminals of a Zener diode is reversed and the potential reaches the Zener Voltage knee voltage the junction breaks down and the current flows in the reverse direction. The diodes are classified into different types based on the working principle and its characteristics like Zener diode LEDs constant current diodes generic diodes varactor diodes tunnel diodes ideal diode laser diodes photo.
However a reverse current flow typically means that the diode is overloaded voltage-wise and has failedperhaps violently. These types of diodes are commonly known as Zener Diodes and are discussed in a later tutorial. Now in case the input voltage is altered lets imagine from 80 to 90 V will cause the voltage drop across the Zener to still maintain the rated 47 V.
A Zener diode is a special type of diode designed to reliably allow current to flow backwards when a certain set reverse voltage known as the Zener voltage is reached. We need to determine the nominal input voltage and it must be a few volts greater than V Z. The detailed process of a diode can be somewhat challenging to understand since it involves an understanding of quantum mechanics.
A diode is a one-way conductor. Zener diodes however are designed to allow voltage flow in forward-biased direction in the same manner as P-N diodes. Normal p-n junction diodes will fail if enough voltage is applied in the reverse biased direction allowing current to flow.
When the capacitor gets fully charged charge on the capacitor depending upon the value of R it discharges through Zener diode Z. The voltage drop across the diode always remains constant irrespective of the applied voltage and this feature of the Zener diode makes it suitable for voltage regulation. For this example we will use V IN 8V.
The Operation of a Diode. Zener diodes are manufactured with a great variety of Zener voltages and some are even variable. A Zener Diode also known as a breakdown diode is a heavily doped semiconductor device that is designed to operate in the reverse direction.
As a rule of thumb we choose the nominal current through the zener to be 10 of the required output load current or 6mA. While in many instances the cause is harmless blood in urine hematuria can indicate a serious disorder. OR SEVERAL MODULE FOR HIGHER VOLTAGE CURRENT.
These diodes also pass current in the forward bias region similarly to a standard p-n. Power can flow in the reverse biased direction over diodes. Look around the board for a label Z or ZD near a component that appears to be a zener diode.
However Zener diodes are designed to exhibit this behavior at a set voltage level as part of their normal operation. Using just a single transistor and few zener diodes you can get different voltages ranging from 5 V to 10 V from a supply input of 12 V. Semiconductor diodes are the most common type of diode.
The diffusion current I S is dependent on the doping level of n-type and p-type impurities the area of the diode and very much on temperature. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes releasing energy in the form of photonsThe color of the light corresponding to the energy of the photons is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. If we had oriented the diode in the normal way so as to be forward-biased it would only drop 07 volts just like a regular rectifying.
A zener diode often has a label containing the letter Z. Some Zener diodes have a sharp highly doped pn junction with a low Zener voltage in which case the. Diode converts AC into DC Can I use IN4007 RECTIFIER DIODE.
This means that an LED will pass current in its forward direction but block the flow of current in the reverse direction. When over-voltage protection is required for switch mode power supplies SMPS the clamp and crowbar techniques are less widely used because of the power dissipation requirements and the possible size and cost of the components. Simple Overvoltage Protection Circuit Using Zener Diode.
The diode is reverse-biased and intentionally so. D can label a zener because its a diode although wed like to find out what convention is used on your board. Whereas in reverse bias there will be an occurrence of minimal leakage current.
Thus when reverse biased the diode behaves much like an open switch. When a diode is connected in a Forward Bias condition a negative voltage is applied to the N-type material and a positive voltage is applied to the P-type material. If this external voltage becomes greater than the.
Zener diode placement knowledge can make or break a design. Although in the real world diodes can not achieve zero or infinite resistance. Either way its important to determine the reason for the bleeding.
The biggest practical difference is that a Zener diode is made to break down in a useful and predictable way while a rectifying diode is made to predictably not break down. Instead a diode will have negligible resistance in one direction to allow current flow and very high resistance in the reverse direction to prevent current flow. Why Zener Diodes Work in Reverse Bias.
A selection of light emitting diodes. Earlier I provided a more simplified explanation of standard diode operation. When there is an increase in the reverse voltage up to the breakdown voltage then.
So if you buy a Zener diode thats designed to regulate to 12V then you can figure that if you arrange for it to get the right current in the reverse direction youll. This gives a pulse to the primary and thereby secondary of the transformer T 2. A diode is effectively like a valve for an electrical circuit.
In the same way it obstructs the current flow during reverse bias in which it gives very high resistance. Zener Diodes with glass or black resin encapsulation. The below shown diagram and the chart shows how the transistor the zener diode and the biasing resistor can be configured for implementing the simple transistor regulator circuit.
Zener Diode Operation Please take note of the Zener diodes orientation in the above circuit. The Light Emitting Diode or LED as it is more commonly called is basically just a specialised type of diode as they have very similar electrical characteristics to a PN junction diode. We first must choose a zener diode V Z 47V which is the nearest value available.
If you find one then it suggests your cracked diode is a plain type. Zener diode regulator circuit Zener voltage 126V. A - simple Zener diode b - higher current with transistor buffer Voltage limiting.
Does anyone have a schematic for a pulse charger once the cap has reached a preset voltage it would discharge into a charging circuit. And when forward biased for currents of about 10 mA or greater the diode gives a nearly constant voltage drop of 07 V. During positive half cycle capacitor C 2 gets charged through diode D 1 pot R and diode D 4.
Zener diode functions in a similar way as of diode when operated in forwarding bias condition. In an absence of a load across the output of the zener diode a 47 Volts can be seen dropped across the Zener diode while a cut off 24 Volts is developed across resistor R. Yellow and green indicator LEDs an infra-red photodiode a 5mm warm white LED and a 10mm high luminosity blue LED.
A light-emitting diode LED is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it. A 51V Zener diode blocks current to flow in the opposite direction up to 51V If the voltage is greater than 51V through the Zener diode it allows the current to pass through it. A small signal silicon diode.
Can you use the 1N4007 diodes AND a larger cap.
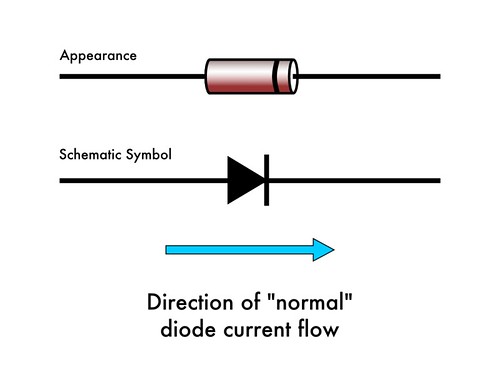
Basics Introduction To Zener Diodes Evil Mad Scientist Laboratories
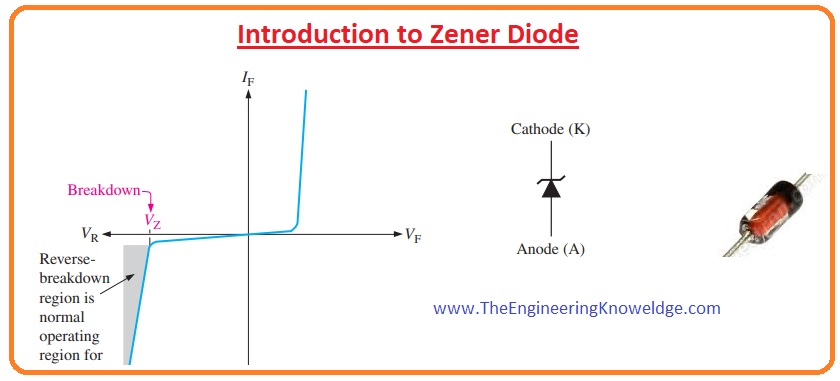
Introduction To Zener Diode Working Application Pinout Definition The Engineering Knowledge
What Is The Actual Symbol For Zener Diode Quora

What Is A Zener Diode And How Does It Work Tutorials Circuitbread

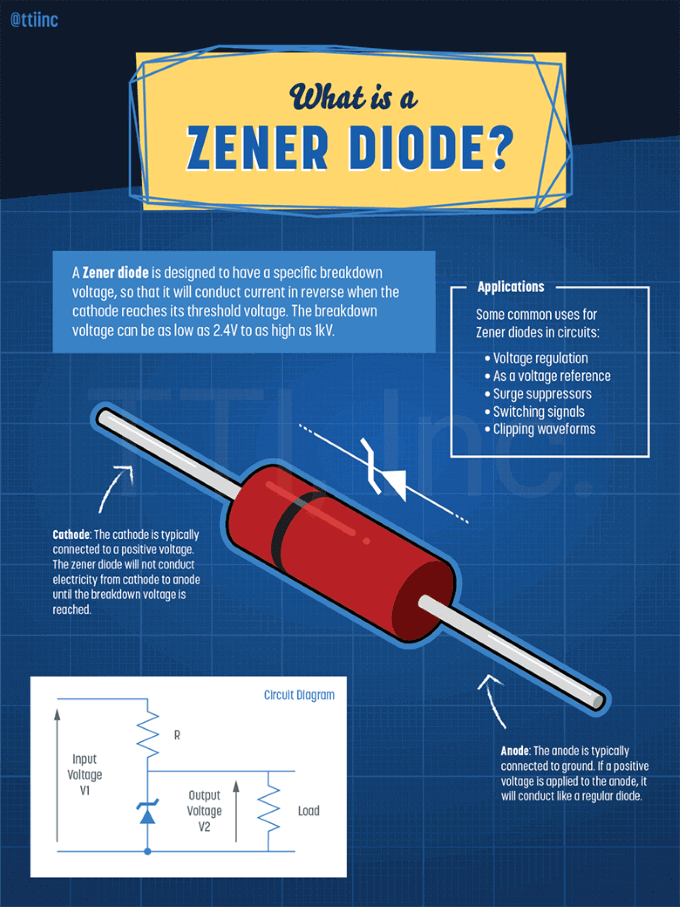
Zener Diodes Infographic Tti Inc

Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial
Do Zener Diodes Have Polarity Quora

What Is Zener Diode What Are Its Operations And Characteristics Circuit Schools
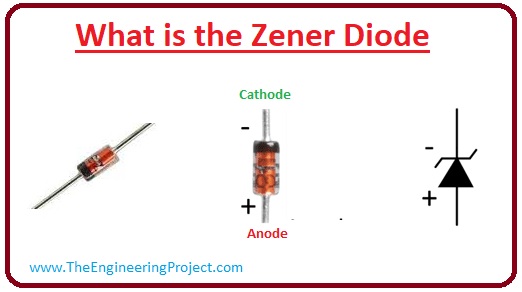
What Is Zener Diode Definition Symbol Working Applications The Engineering Projects
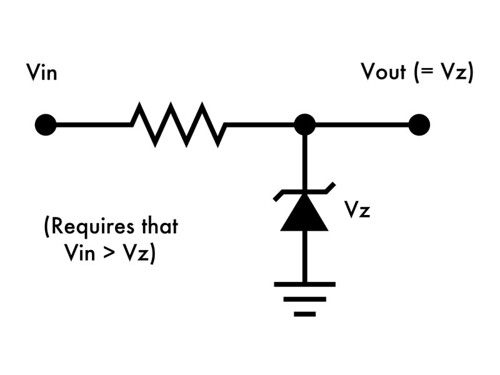
Basics Introduction To Zener Diodes Evil Mad Scientist Laboratories
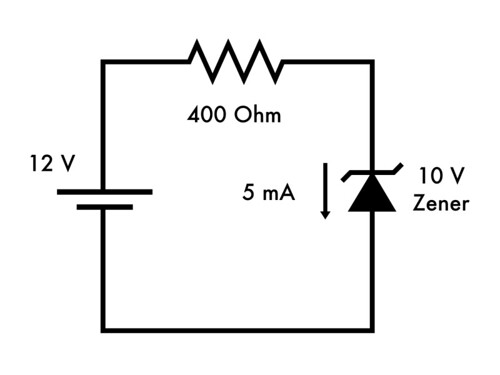
Basics Introduction To Zener Diodes Evil Mad Scientist Laboratories

Basics Introduction To Zener Diodes Evil Mad Scientist Laboratories
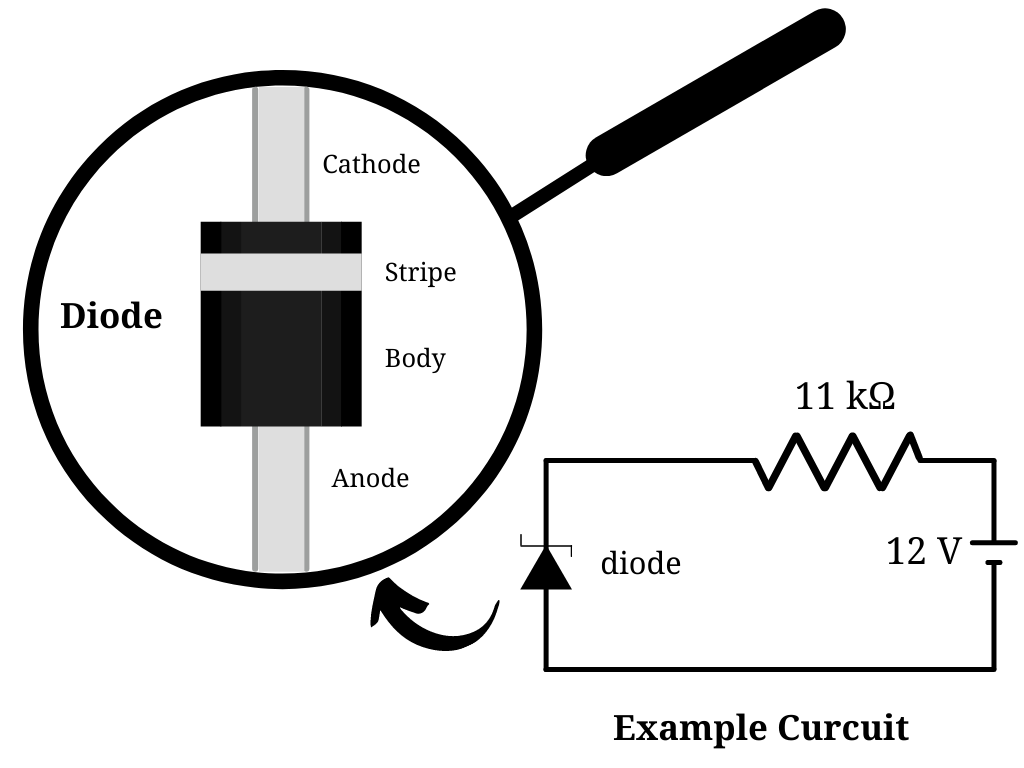
The Zener Diode What It Is How It Works And It S History Derf Electronics

What Are Zener Diodes Instrumentationtools
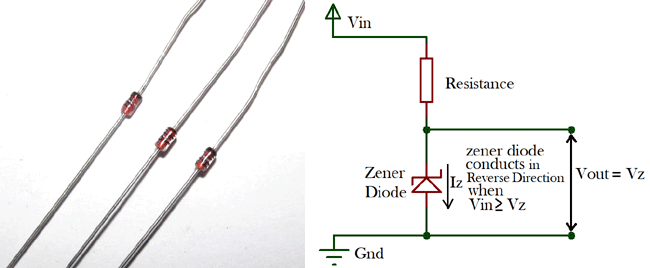
What Is Zener Diode Operation Principle Types Uses Of Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Waveform Clipper And Voltage Shifter

Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial

Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial
Where Are Zener Diodes Used Quora

What Is A Zener Diode And How Does It Work Intermediate Electronics Youtube